- Home
-
Products
- Frequency Converter
-
General-Purpose Inverter
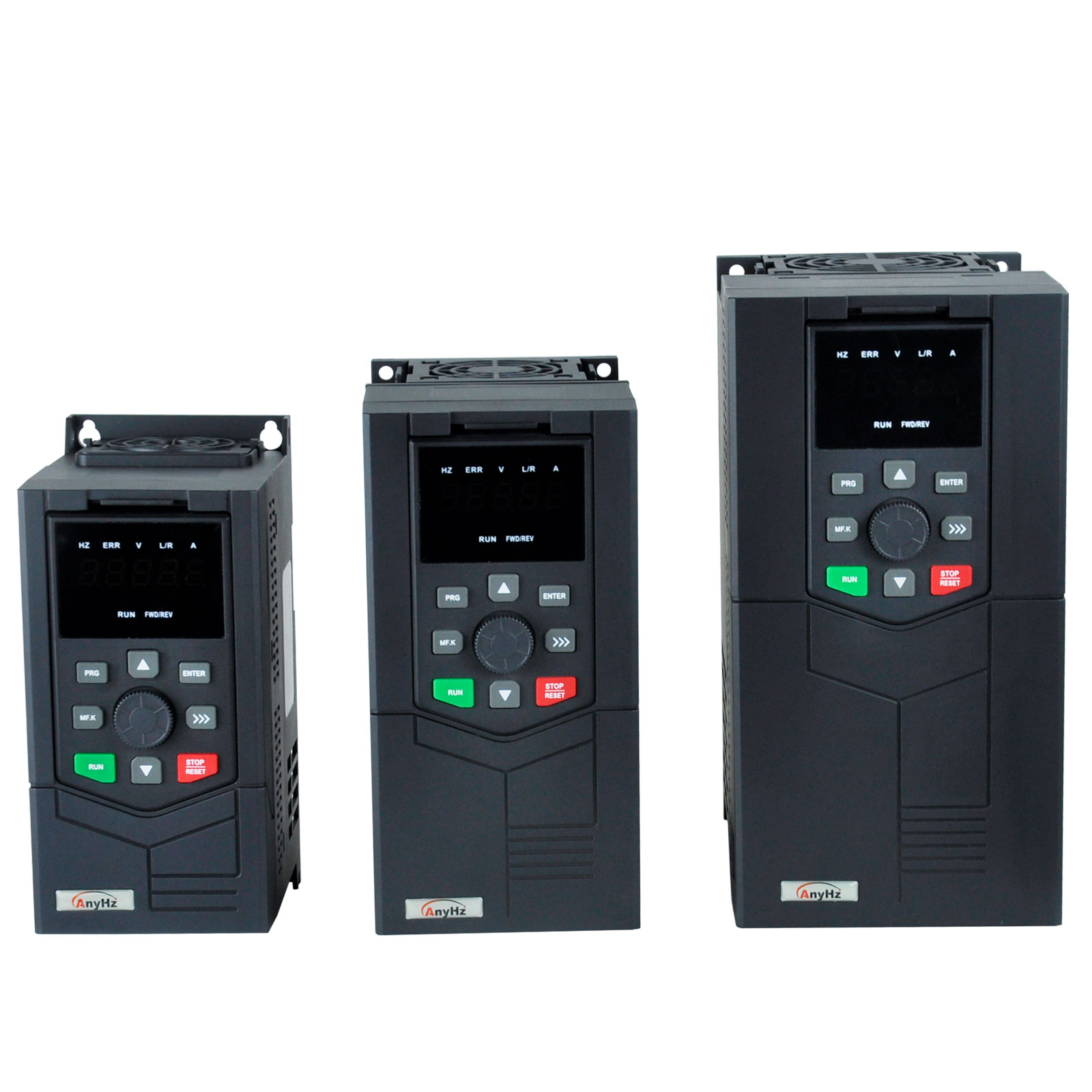

FST-650L High performance vector universal frequency converter
High performance vector, low speed high torque output, rich and powerful functions, stable performance
Learn More + - Dedicated frequency converter
-
Inverter Cabinet OEM
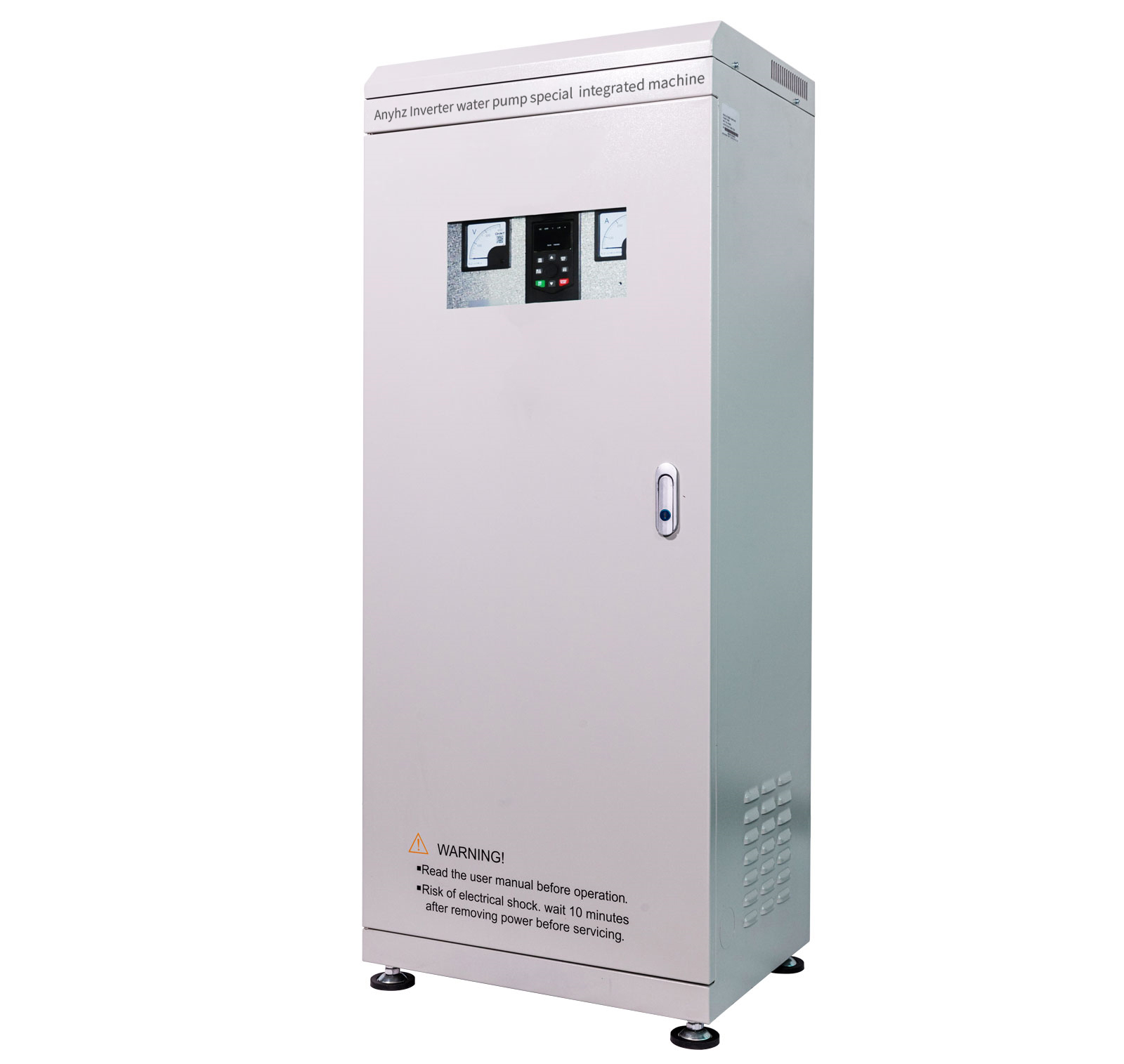

Water pump dedicated frequency converter all-in-one machine
To meet the personalized and industry-specific needs of customers, it adopts a frequency conversion energy-saving control integrated cabinet mode
Learn More + - Drive Peripheral
-
HMI Display Screen

HMI display screen
HMI display screens are a key bridge connecting OT and IT information in the industrial field, making factory production management clearer and more transparent, and making equipment services more timely and efficient!
Learn More + -
Soft Starter
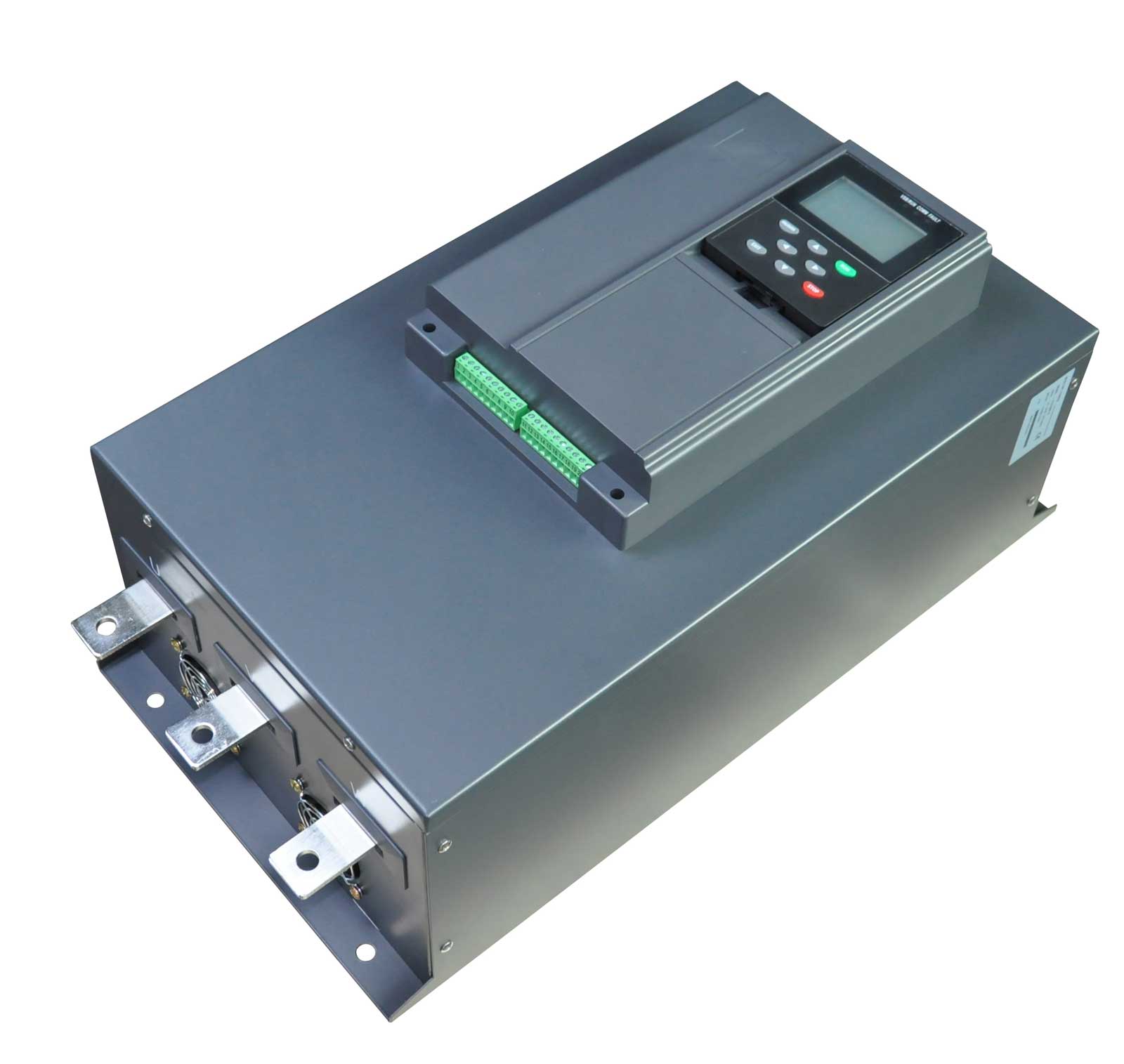

FST-3000 series built-in bypass soft starter
The new generation of built-in bypass multifunctional intelligent soft starter has strong anti-interference performance, complete protection functions, as well as multiple control modes and support for remote communication protocols
Learn More + -
Drive braking
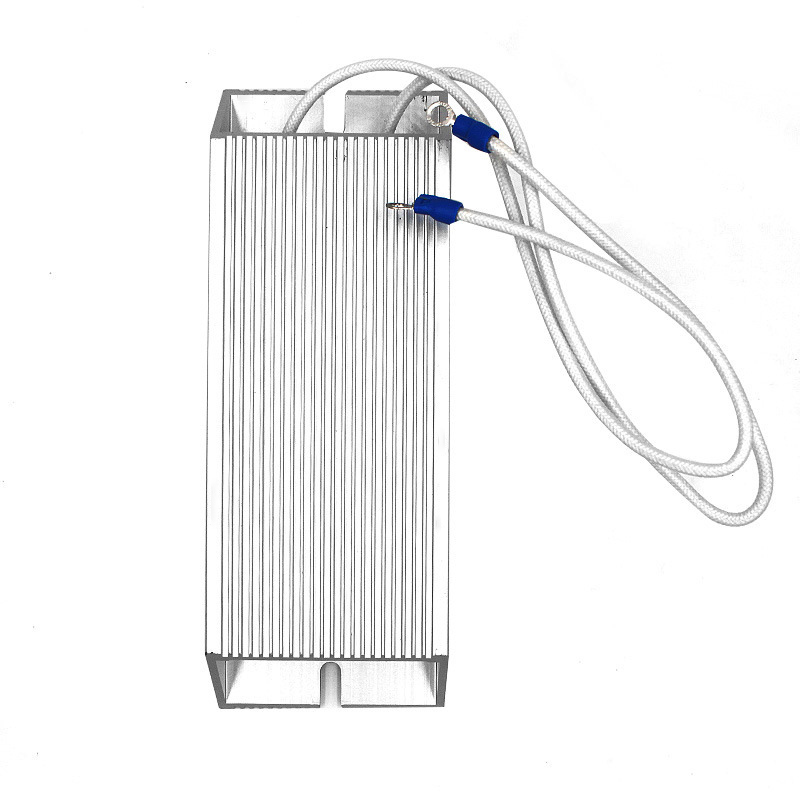
Fixde Resistors
Elevator brake resistor, frequency converter brake resistor, servo resistor, aging resistor, braking unit resistor, driving resistor
Learn More + -
Wave Filter
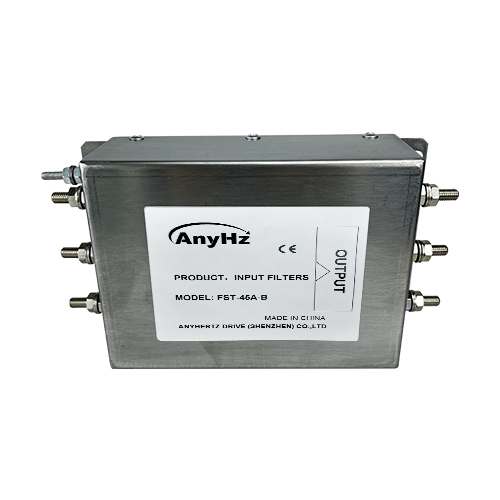

FST series input/output filters
Effectively suppress conducted interference propagating along power lines and reduce radio frequency interference generated by electronic devices
Learn More +
- Industry application
- About Us
- Service and Support
- Contact Us





 Contact Us
Contact Us


